Introduction to Paving Materials Asphalt
When it comes to building roads, driveways, and parking lots, paving materials asphalt is one of the most widely used solutions. Known for its affordability, flexibility, and quick installation, asphalt has been the backbone of modern infrastructure for decades.
Unlike rigid paving materials like concrete, asphalt provides a smooth, flexible surface that can withstand heavy loads and changing weather conditions. From residential driveways to major highways, asphalt remains a cost-effective and durable paving material trusted worldwide.
What Is Asphalt?
Asphalt, often referred to as bitumen, is a mixture of aggregates (sand, stone, and gravel) bound together by a petroleum-based binder. When heated and compacted, this mixture creates a durable, smooth, and water-resistant surface suitable for various paving applications.
The Role of Asphalt in Modern Paving
Today, asphalt covers over 90% of paved roads in the U.S. due to its cost-effectiveness and adaptability. Beyond roadways, it is also used for airport runways, playgrounds, and sports courts, making it one of the most versatile paving materials available.
Types of Asphalt Paving Materials
Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA)
- Standard for highways and high-traffic areas
- Durable and weather-resistant
- Requires high-temperature installation
Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA)
- Uses lower temperatures for mixing
- More energy-efficient and eco-friendly
- Reduces emissions during installation
Cold Mix Asphalt
- Best for temporary repairs and patching potholes
- Can be applied in colder weather
- Not ideal for heavy-traffic areas
Porous Asphalt
- Allows water to drain through the surface
- Reduces stormwater runoff and flooding
- Popular in sustainable construction projects
Key Benefits of Asphalt as a Paving Material
Affordability and Cost-Effectiveness
Asphalt is significantly cheaper to install than concrete or stone. Its quick installation also reduces labor costs.
Durability and Load-Bearing Capacity
Properly maintained asphalt surfaces can last 15–20 years, supporting heavy vehicles and traffic.
Quick Installation and Usability
Unlike concrete, which requires curing, asphalt can be used within 24–48 hours after installation.
Recyclability and Environmental Benefits
Asphalt is 100% recyclable, making it one of the most eco-friendly paving materials available.
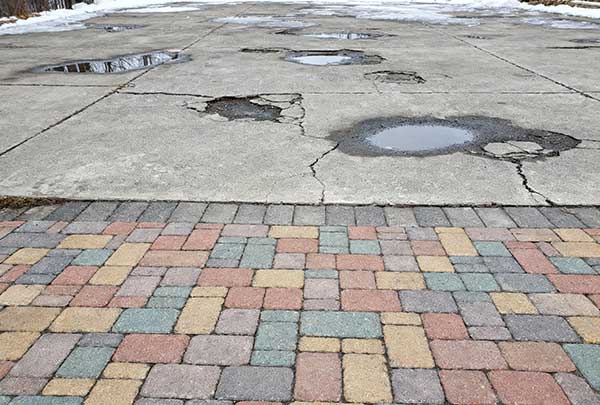
Limitations of Asphalt Paving
Shorter Lifespan Compared to Concrete
While asphalt is cost-effective, it generally lasts 15–20 years, compared to concrete’s 30–40 years.
Regular Maintenance Requirements
Asphalt requires sealcoating, crack filling, and periodic resurfacing to maintain performance.
Vulnerability to Extreme Temperatures
- In hot climates, asphalt can soften and rut under heavy loads.
- In cold climates, freeze-thaw cycles can cause cracking and potholes.
Best Applications of Asphalt Paving
Residential Driveways
Asphalt is affordable, quick to install, and provides a smooth black finish that enhances curb appeal.
Roads and Highways
Over 90% of U.S. highways use asphalt due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to handle heavy traffic.
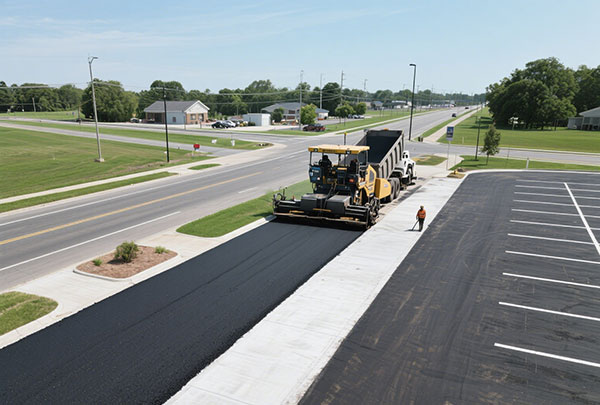
Parking Lots
Asphalt is ideal for large parking areas, offering durability and easy maintenance.
Recreational and Commercial Spaces
Playgrounds, running tracks, and airport runways often rely on asphalt for its flexibility and shock-absorbing properties.
Installation Process of Asphalt Paving
Site Preparation and Grading
- Remove existing materials.
- Ensure proper grading for drainage.
Laying the Base Course
- Add a crushed stone foundation for stability.
- Compact the base to prevent sinking.
Asphalt Application and Compaction
- Apply hot or warm asphalt mix in layers.
- Compact with heavy rollers to ensure density.
Curing and Finishing
- Asphalt sets quickly but requires 24–48 hours before use.
- Sealcoating can extend lifespan and improve appearance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Asphalt Paving
- Skipping proper drainage planning, leading to pooling and early deterioration.
- Thin asphalt layers, which reduce durability.
- Neglecting compaction, causing surface weakness.
- Poor maintenance, accelerating cracks and potholes.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Asphalt Surfaces
Sealcoating
Apply every 2–3 years to protect against UV rays, water, and chemicals.
Crack Filling and Pothole Repair
Early repairs prevent cracks from spreading and avoid costly resurfacing.
Seasonal Care Practices
- In winter, use plastic shovels instead of metal to avoid surface damage.
- In summer, avoid parking heavy vehicles on freshly laid asphalt.
Comparing Asphalt with Other Paving Materials
Asphalt vs. Concrete
- Asphalt: Cheaper, faster installation, requires more maintenance.
- Concrete: Longer lifespan, more expensive, slower to install.
Asphalt vs. Interlocking Pavers
- Asphalt: Affordable and quick but limited in design.
- Pavers: Highly customizable and repairable but costlier.
Asphalt vs. Gravel
- Asphalt: Smooth, durable, and weather-resistant.
- Gravel: Low cost but requires frequent replenishing and maintenance.
Environmental Considerations of Asphalt
Asphalt Recycling (RAP – Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement)
- Asphalt is the most recycled material in the U.S.
- Recycled asphalt reduces demand for raw materials and lowers costs.
Porous Asphalt for Water Management
- Helps reduce stormwater runoff.
- Allows natural water infiltration to recharge groundwater.
Cost Factors of Asphalt Paving
Material Costs
- Asphalt typically costs $2–$5 per square foot.
Installation Costs
- Professional installation ranges from $7–$15 per square foot, depending on project size and thickness.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs
- Regular sealcoating and repairs are necessary but still cheaper overall compared to concrete repairs.
Choosing the Right Asphalt Mix for Your Project
Climate Considerations
- Hot Mix Asphalt: Best for warm climates and heavy traffic.
- Cold Mix Asphalt: Temporary solutions in colder weather.
Traffic Load Requirements
- Thicker, reinforced asphalt is essential for heavy-use highways and parking lots.
Sustainability Goals
- Choose porous asphalt or recycled asphalt mixes for eco-friendly projects.
DIY vs. Professional Asphalt Paving
- DIY: Suitable for small patching jobs using cold mix asphalt.
- Professional Installation: Recommended for driveways, parking lots, and roads to ensure proper grading, compaction, and finishing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How long does asphalt last?
Typically 15–20 years with proper maintenance.
Q2. How soon can I use a new asphalt driveway?
Light use is possible after 24–48 hours.
Q3. Does asphalt require sealing?
Yes, sealcoating every 2–3 years extends its life and prevents damage.
Q4. Is asphalt eco friendly?
Yes, asphalt is 100% recyclable, and porous asphalt supports sustainable water management.
Q5. Which is cheaper, asphalt or concrete?
Asphalt is generally cheaper upfront, but concrete lasts longer with fewer repairs.
Q6. Can asphalt handle heavy vehicles?
Yes, with proper thickness and base preparation, asphalt can handle heavy trucks and machinery.
Conclusion: Why Paving Materials Asphalt Remains a Popular Choice
As one of the most widely used paving materials in the world, asphalt combines affordability, speed of installation, and durability. While it may require regular maintenance, its cost-effectiveness and recyclability make it a sustainable option for residential, commercial, and public projects.
From driveways and parking lots to highways and runways, asphalt continues to play a vital role in modern infrastructure. With proper care and professional installation, asphalt remains a reliable, eco-friendly, and smart investment for paving needs.
👉 If you want a paving material that balances budget, performance, and sustainability, asphalt is an excellent choice.